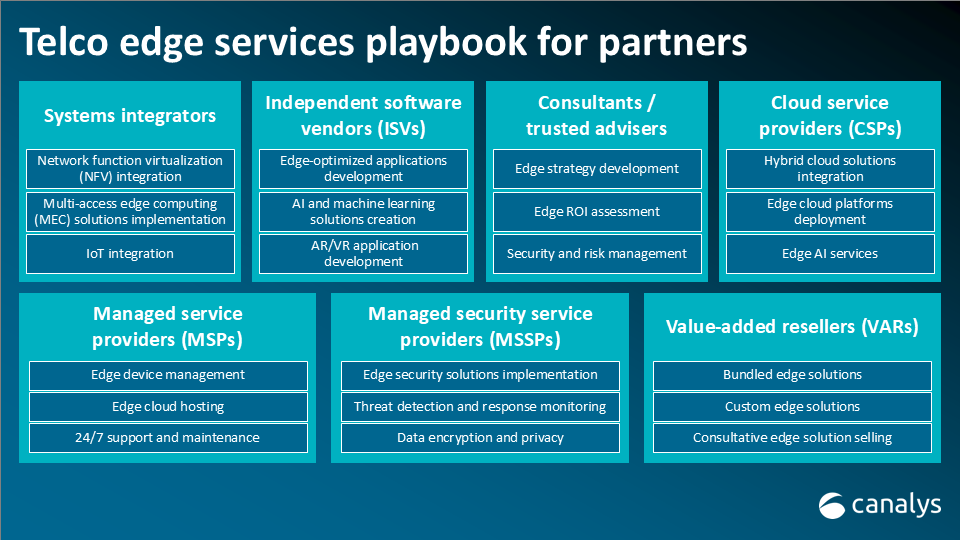
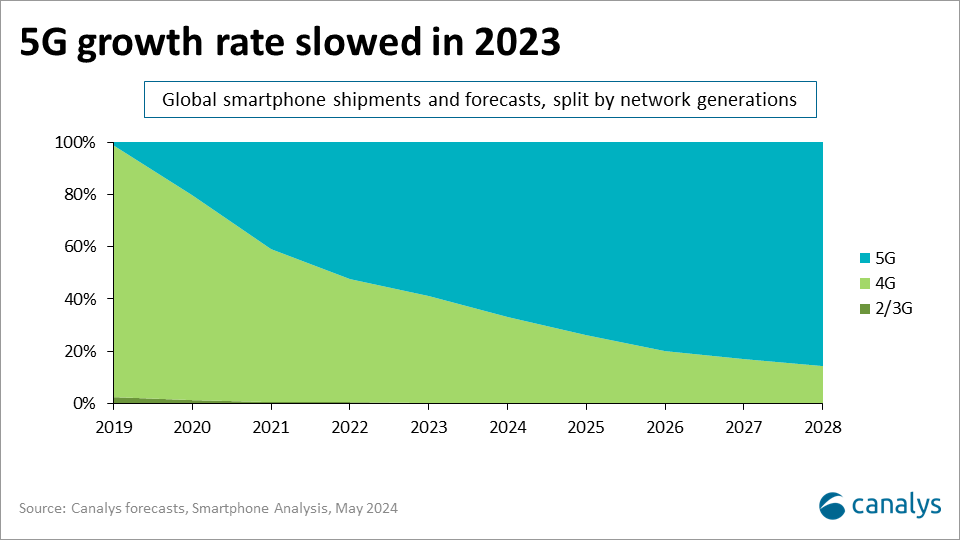
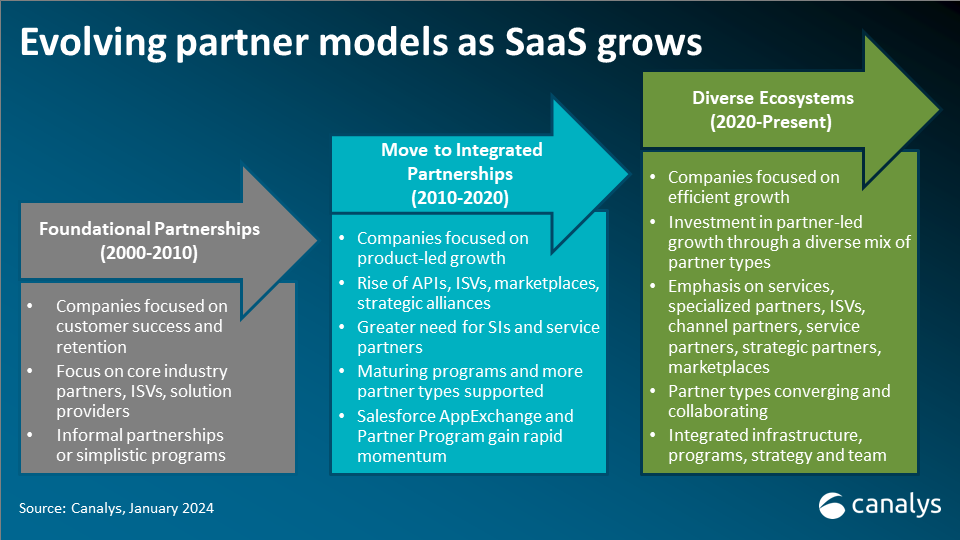
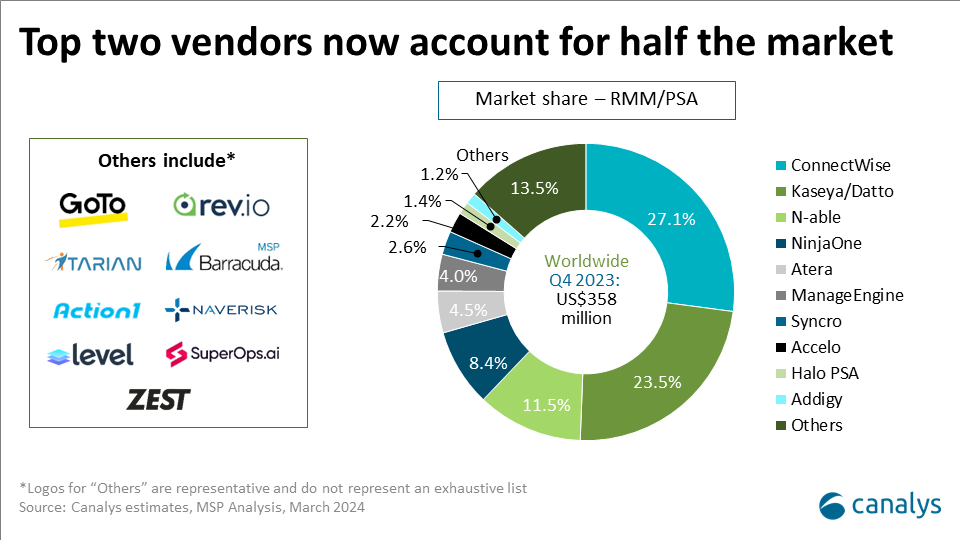
Canalys is part of Informa PLC
This site is operated by a business or businesses owned by Informa PLC and all copyright resides with them. Informa PLC’s registered office is 5 Howick Place, London SW1P 1WG. Registered in England and Wales. Number 8860726.
eSIM watches in China: the need for use case exploration
In the short and mid-term, adding eSIMs to basic watches can help increase shipments in the mainland China market, but in the medium to long-term, there are challenges due to limited use cases.

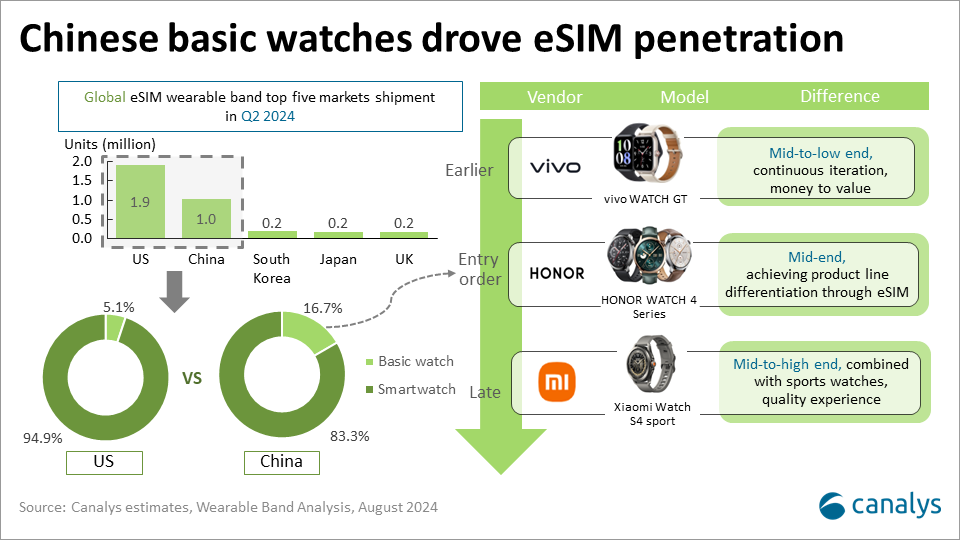
eSIM is one of the key connectivity solutions for enabling independent communication in wearable bands, creating independent mobile devices second only to smartphones. Furthermore, AI integration augments eSIM's ability to ensure continuity and reliability across numerous IoT device connections, establishing eSIM's crucial role in ecosystem integration. According to Canalys estimates, in Q2 2024, the US led in eSIM-enabled wearable band shipments with 1.9 million units, accounting for 33.9% of all wearable band shipments. China followed with 1.0 million eSIM device shipments, representing 10.8% of all wearable bands shipped. However, the eSIM penetration in the US market comes from smartwatches, mainly boosted by Apple and Samsung. In contrast, the Chinese market presents a different scenario, where domestic vendors' eSIM basic watches contribute significantly to the growth in eSIM wearable bands.
In China, the main players offering eSIM basic watches are vivo, HONOR and Xiaomi. They belong to the smartphone ecosystem and each has introduced one or more eSIM basic watches, employing distinct strategies:
- vivo, one of the early players in the eSIM basic watch market, targets the mid- to low-end and continuously iterates its offerings. The currently available eSIM basic model, Watch GT, starts at a price as low as CNY799 (US$113), features AI elements that enhance smartphone connectivity and offers a long battery life, providing consumers with a value-for-money option.
- HONOR focuses on the mid-tier segment. Beyond incorporating eSIM functionality into its Watch 4 series, HONOR added dual standby (for receiving texts and missed-call notifications from two lines), ECG (available on the Watch 4 Pro model), and WeChat functionality to differentiate it from other competing products.
- Xiaomi pursues a high-end strategy with eSIM. The Watch S4 Sport, features eSIM functionality, and is designed for users who appreciate technology and are looking for convenience in a sports watch, offering a smart option in the wearable market.
Integrating eSIM functionality into basic watches makes the feature affordable, broadening consumer access and encouraging the adoption of eSIM technology in the wristwatch market. However, from a mid-to long-term perspective, several challenges hinder growth of eSIM basic watches:
- Limited application scenarios: eSIM wearables are not fully independent from smartphones in typical user scenarios. In most situations, eSIM addresses specific communication needs or situations where smartphone use is inconvenient, resulting in limited usage frequency. Moreover, basic watches typically lack a complex application ecosystem and robust processing capabilities, which poses challenges for high-frequency applications such as real-time navigation, media streaming, and ride-hailing apps. This necessitates further development by vendors to expand the application scenarios of eSIM functionality and increase user stickiness with this feature.
- Cost-effectiveness considerations: Vendors can experience a short-term sales boost by adding eSIM to basic watches, but they must invest in backend systems and platform development to maintain service quality. Lowering eSIM watch prices might not convert to actual sales, limiting return on investment and hampering future product innovation and market competitiveness. For consumers, eSIM basic watches are relatively affordable but add ongoing cellular subscription costs for limited communication features. This creates a reoccurring cost in a market usually driven by one-time purchases, requiring vendors to offer exceptional services and experiences that exceed expectations to convince consumers.
- Telecom operator restrictions: Chinese network operators have hesitated to promote eSIM services, with limited investment in developing appealing plans, branding, and online service enrollment. The lack of standardization among service providers has negatively impacted user experience and market penetration. For basic watches, low prices and thin margins may discourage carriers from promoting eSIM services, limiting its impact within operator channels.
In summary, while integrating eSIM functionality into basic watches injects new vitality into the wearable band market, the mid-to-long-term development of eSIM technology in this segment faces challenges such as limited application scenarios, cost-effectiveness considerations, and operator restrictions. As technology matures and the market environment improves, eSIM basic watches are expected to expand their application boundaries further, providing users with a more diverse and enriched wearable experience.