Introduction to financing the future of smartphone access in Kenya’s informal economy report
11 August 2025
With a combined permissioned audience of 50+ million professionals, TechTarget and Informa Tech’s digital businesses have come together to offer industry-leading, global solutions that enable vendors in enterprise technology and other key industry markets to accelerate their revenue growth at scale.
The following is an extract from a comprehensive 15-page report into the complex financing value chain of smartphones in Kenya, exploring one of Africa’s most successful case studies in device financing. Access the full report here.
Kenya’s smartphone financing value chain market offers a live blueprint for tackling one of the most persistent challenges in emerging economies—affordability. While global smartphone shipment growth remains subdued, value growth is being driven by rising average selling prices (ASPs) and financing-led upgrades. For markets where income patterns, credit access, and device affordability remain misaligned, financing is no longer an optional lever—it is becoming a core distribution strategy.
Smartphones have become indispensable in Kenya, connecting people to education, healthcare, commerce, and financial services. By March 2025, the country had 42.4 million smartphones in use, accounting for 80.8% of mobile connections. Yet, affordability remains the largest barrier, especially for low-income and informally employed consumers. Even in 2024, 59% of mobile phone shipments were still feature phones, leaving a significant portion of the population excluded from full digital access. This affordability gap has triggered a wave of financing-led solutions designed to bring smartphones within reach, particularly in rural and underserved markets.
Kenya’s smartphone average selling price (ASP) has nearly tripled in local currency since 2019, from KES5,955 to KES18,979 in Q2 2025. Currency depreciation, higher import duties, rising global component costs, and the curtailment of grey imports have all contributed to this jump.
As prices rise, the share of smartphones below US$100 has fallen to 32%, while mid-tier devices between US$100 to US$199 now make up over half of all shipments.
This shift is pushing the Kenyan smartphone industry toward financing-led upgrades.
Traditional postpaid models fail in rural and informal segments, where 80% of the workforce earns daily or weekly wages. Instead, the market has embraced daily micro-payment plans of as little as KES30 to 50, combined with device-lock technology and mobile money integration.
Financing solutions do more than enable ownership—they accelerate the shift from feature phones to smartphones, expand digital participation, and build a foundation for financial inclusion.
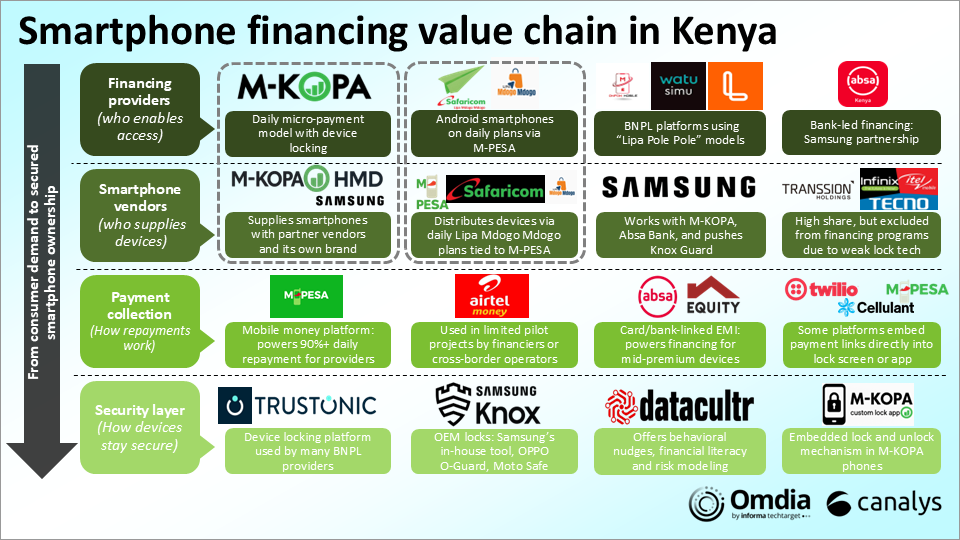
Kenya’s smartphone financing ecosystem is not just a patchwork of lenders, vendors, and telcos—it is a layered architecture built to match the realities of an informal, mobile-first economy.
Sales channels are pivotal in bridging financing providers and end users. Financing companies typically collaborate with local dealers and retailers, who handle both the sale of devices and the facilitation of financing plans. These dealers source inventory through their existing distributor networks (such as Redington, Guree, and Mitsumi) rather than directly from manufacturers. This channel-led approach leverages the trust and accessibility of local sellers, enabling frictionless onboarding into financing schemes.
Behind the simple act of enabling consumers to pay KES50 a day lies an ecosystem of secure locks, dynamic credit rules, real-time mobile money integrations, and behavioural triggers.
Understanding the complex nature of the financing value chain is key for any players inside it to succeed and for any companies seeking to replicate the best practices into other markets.
The full report provides an in-depth breakdown of all four layers in this value chain, explaining how financing is structured from access to security.
It also provides examples of the key players and technology enablers shaping each stage. Companies mentioned include: Samsung, OPPO, TRANSSION, TECNO, itel, Infinix, Samsung, HMD Global, M-KOPA, Watu Simu, LOOP, Xiaomi, Safaricom, Airtel Kenya, M-PESA, Airtel Money, Trustonic, Datacultr, Twilio, Cellulant, Redington, Guree, Mitsumi, and Absa Bank Kenya.
Kenya’s smartphone financing value chain market offers a live blueprint for tackling one of the most persistent challenges in emerging economies—affordability. While global smartphone shipment growth remains subdued, value growth is being driven by rising average selling prices (ASPs) and financing-led upgrades. For markets where income patterns, credit access, and device affordability remain misaligned, financing is no longer an optional lever—it is becoming a core distribution strategy.
This makes the topic highly relevant for:
With affordability challenges set to persist, financing will be a critical growth driver across emerging markets, enabling vendors and ecosystem players to unlock new value pools even in stagnant shipment environments.
If you already subscribe, access the full report here. If not, contact us to access the full report, arrange a private briefing, or explore tailored insights. The complete report includes detailed vendor strategies, deep dives on M-KOPA and Safaricom, risk analysis, and strategic recommendations for applying these lessons to other emerging markets.
Discussed in the report: Smartphone financing | Emerging markets | Kenya mobile market | Mobile money | Device affordability | Micro-payments | Pay-as-you-go (PAYGo) Digital inclusion | Financing value chain | Daily payment plans | Informal economy | Device locking technology | Mobile-first economy | BNPL (Buy Now Pay Later) | Telco-led financing | Vendor financing strategy | Feature phone to smartphone migration | Credit risk management | Mobile device distribution | Digital collateral | Financing ecosystem scalability | Rural smartphone access ASP (Average Selling Price) growth | Currency depreciation impact | Financing-driven upgrades.