Samsung Galaxy S24: unveiling Samsung’s AI-driven future roadmap
18 January 2024
Canalys is part of Informa PLC
This site is operated by a business or businesses owned by Informa PLC and all copyright resides with them. Informa PLC’s registered office is 5 Howick Place, London SW1P 1WG. Registered in England and Wales. Number 8860726.
CES 2024 witnessed a return to pre-pandemic attendance levels and a focus on Software-Defined Vehicles (SDV) with AI, software, cloud and tools for EV development. Key highlights include Qualcomm and NVIDIA's competition in SoCs for digital cockpits and ADAS fusion, Intel's strategic shift in the EV market with AI-powered SoCs, and an open chiplet platform. This blog provides a summary and insights on crucial announcements made by industry leaders.


CES 2024 welcomed a return to pre-pandemic attendance levels with 135,000 participants. A dominant theme was Software-Defined Vehicles (SDV), focusing on AI, software, cloud and tools for accelerating EV development. Notable absentees included Detroit’s big three, but Honda, Hyundai and KIA took the spotlight. While Chinese carmakers had a limited presence, specialized Chinese suppliers in ADAS and digital cockpits were present. Canalys received inquiries from key exhibitors regarding the Chinese market.
The automotive semiconductor sector witnessed heightened competition, marked by AMD’s entry, Intel’s new System-on-Chips (SoCs) and its acquisition of Silicon Mobility. NVIDIA secured design wins with Chinese EV manufacturers and Qualcomm emphasized industry leadership and platform enhancements.
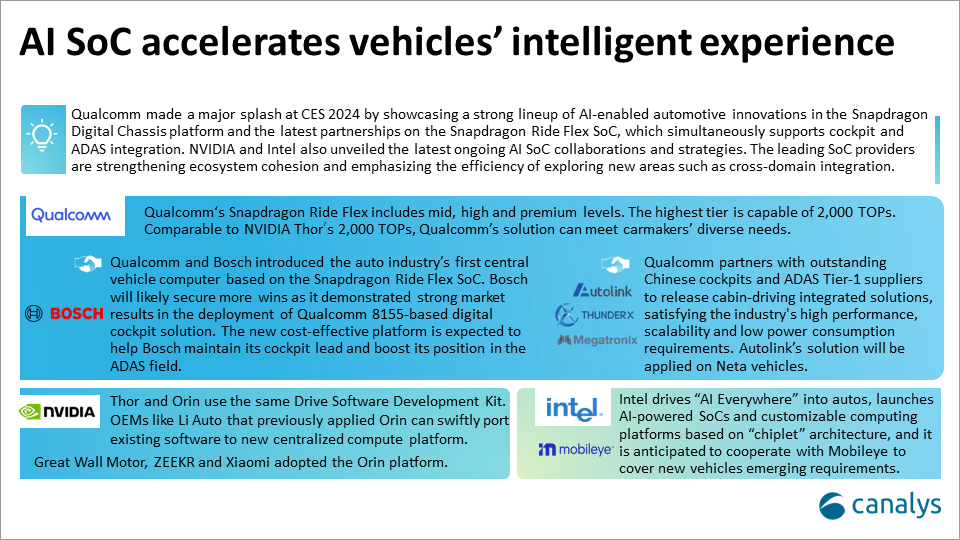
At the CES 2024 exhibition, both Qualcomm and NVIDIA highlighted the latest ongoing collaboration process of SoCs, which supports digital cockpit and ADAS features. In the transition from domain controllers to central computing in the new EV electronic/electrical architecture, these two companies, dominant in developing high-performance chips for digital cockpits and assisted driving with high development thresholds, emphasized the inheritability between new and old solutions. They aim to reduce the sunk costs of automotive OEM iterations, solidify their respective product ecosystems and strengthen their influence in each other’s core markets.
Qualcomm and Bosch jointly unveiled the world’s first cross-domain in-vehicle central computing platform based on Qualcomm Snapdragon Ride Flex (with computing power scalable up to 2,000 TOPs). This product launch brings positive impacts to both parties, as Bosch leverages the robust performance in the digital cockpit market generated by the deployment of the Snapdragon SA8155P, leading Qualcomm to gain more market share. Simultaneously, the new cost-effective platform is expected to help Bosch maintain its leading position in the digital cockpit sector while enhancing its influence in the assisted driving field.
In addition, Qualcomm also showcased its latest cockpit-driving integrated solutions with Chinese solution providers such as Autolink, Megatronix and Thunderx. The Connected Cars solution will debut on the Neta Shanhai Platform 2.0’s model.
NVIDIA announced that the Thor chip platform (with computing power of up to 2,000 TOPs) would be applied in Li Auto’s next-generation models. Furthermore, Great Wall Motors, ZEEKR and Xiaomi have adopted the Orin chipset to develop next-generation assisted driving systems. NVIDIA’s strategy is straightforward in promoting cockpit-driving integrated solutions, offering only a single ultra-high compute platform solution. By ensuring Thor is compatible with the same software development kit (SDK) as Orin, NVIDIA aims to reduce the sunk costs for automakers choosing Orin.
In contrast to NVIDIA’s focus on the integrated cabin and driving field, Qualcomm concentrates on meeting OEMs’ long-term strategic development needs in different stages of intelligent development by combining different chips to form scalable low, mid and high-end systems. This approach allows Qualcomm to target a broader range of customer groups.
Intel’s CES 2024 automotive announcements were far more than just product reveals; they marked a strategic shift toward dominating the future of mobility. The acquisition of Silicon Mobility, an EV energy management leader, signals a clear ambition to become a powerhouse in the rapidly growing EV market. This aggressive move not only positions Intel as a direct competitor to established players like NVIDIA and Bosch but also challenges the traditional, closed-loop structure of the industry.
The unveiling of AI-powered software-defined SoCs empowers automakers with the next-generation technology they need to build ever-smarter, autonomous vehicles. But perhaps the most disruptive innovation is the introduction of an open chiplet platform by Intel. This revolutionary system allows for greater flexibility and customization, potentially lowering costs and fostering rapid advancements in automotive technology.
The implications of Intel’s strategy are significant. Their aggressive moves could attract more OEMs and Tier 1 suppliers to their platform, creating a robust ecosystem around their offerings. This, in turn, could further erode the dominance of established players and pave the way for a more open, collaborative automotive landscape. However, success will not be guaranteed. Regulatory hurdles, consumer adoption of new technologies and navigating complex industry dynamics will all play crucial roles in determining the ultimate impact of Intel’s vision.